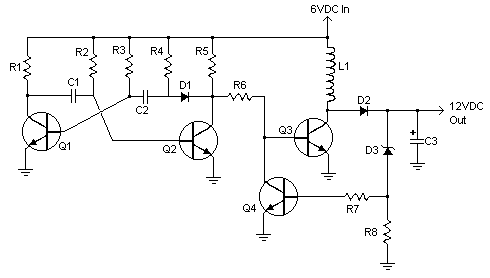
Motorbike Alarm

This simple to build alarm can be fitted in bikes to protect them from being stolen. The tiny circuit can be hidden anywhere, without any complicated wiring. Virtually, it suits all bikes as long as they have a battery. It doesn't drain out the battery though as the standby current is zero. The hidden switch S1 can be a small push-to-on switch, or a reed switch with magnet, or any other similar simple arrangement. The circuit is designed around a couple of low-voltage MOSFETs configured as monostable timers. Motorbike key S2 is an ignition switch, while switch S3 is a tilt switch. Motorbike key S2 provides power supply to the gate of MOSFET T2, when turned on. When you turn ignition off using key S2, you have approximately 15 seconds to get off the bike; this function is performed by resistor R6 to discharge capacitor C3. Thereafter, if anyone attempts to get on the bike or move it, the alarm sounds for approximately15 seconds and also disconnects the ignition circuit. During parki...




+Circuit+Diagram.gif)





+May+be+Sole+Manufacturer+of+(AAPL)+A8+Chips+for+iPhone+6.jpg)